HF and UHF RFID dispute
- Share
- From
- SLONRFID.com
- publisher
- Jacky
- Issue Time
- Sep 17,2013
HF and UHF RFID around the debate between sound technology never stop too , the focus is simply to fight out of a one is better - what is HF or UHF best meet application needs. However , RFID technology is advancing with the times , with each passing day . So, with the traditional way of thinking to analyze HF and UHF RFID technology, there will be no practical significance. Especially with UHF RFID technology, further development , triggered the great debate of the three long-term assumptions also need to re-examine .
Three traditional assumptions
1 . UHF not apply to liquid and metallic materials ;
2 . Use only a short distance to read 13.56 MHz;
3.13.56 MHz level most suitable single product labeling requirements ;
For example , 13.56 MHz technology before someone claims for liquids and metals, but until today, the technology was used in these areas . Moreover , UHF tag with metal improves RF performance. At the same time , HF is also being used in the supply chain , and in the UHF previously only possible to achieve .
In fact, no " best " RFID technology, like do not exist in all cases as a single bar code symbol . RFID frequencies and some products are best suited for a particular environment. We can change the business processes to adapt to different technology, but to change the technical adaptation process is usually not feasible. If you have a good understanding of RFID in a particular environment is how it works , and how RFID can improve their business processes , it is rarely what technology should be used in the end the debate .
Explains why you consider changing the business process is to select the appropriate frequency and RFID applications benefit from the biggest key .
Review : What is the UHF and HF technology
UHF and HF are the general technical categories , but each category has a separate support agreement. HF 13.56MHz band in a more consistent , although the international industry standard for the industry a lot . In the 858-960MHz UHF RFID band has been commercialized. There are also a variety of international standards support, including EPC global Gen 2.
Tag and reader exchange data via a wireless link . Links can be suitable for any band , with different read range and immunity EMF or RF field implementation. HF RFID technology mainly to transfer information through the electromagnetic field , and most UHF systems is through radio waves. Unless otherwise indicated, are talking about here, UHF technology is commonly used in case radio communication technologies .
RFID tag read range that can be achieved depends on the wavelength and frequency , because each has its specific radio frequency wavelength characteristics . Antenna model and the output power is the influence of other leading RFID tag reading range .
Different addition to the frequency , HF and UHF RFID technology, the main difference is the read range . Two different frequencies , the read range , there is very different. 13.56MHz technology, maximum read range of about three feet , and the maximum read range of UHF technology is 30 feet ( 30 meters total ) . Making better able to explain some of the rules of the chart this problem, but these charts only for accurate , useful reference . Table I provides a summary of HF and UHF technology both contrast and common usage .
Table : HF and UHF RFID technology List
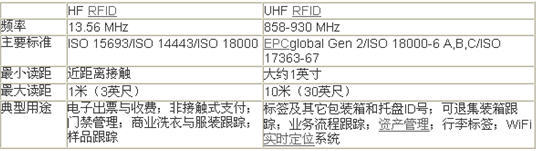
Typical use
Electronic ticketing and tariffs ; contactless payment ; access control ; commercial laundry and clothing tracking ; Sample Tracking
Case and pallet labels and other ID numbers ; retreat container tracking ; business process tracking ; asset management ; luggage tags ; WiFi RTLS
HF RFID technology
HF13.56 MHz technology is quite mature , and access control and contactless payment applications are successful commercialization of RFID initially forms. At 13.56 MHz system tag and reader through the electromagnetic field coupling to transfer information . HF and electromagnetic communication can resist perfectly ordinary business environment exists interference source. We know more about the 13.56 MHz technology drawback is its limited read range , up to about 1 meter. UHF technology is relatively speaking , 13.56 MHz tag reading speed is very slow.
13.56 MHz technology, there are several widely used communication protocols and standards. We are most familiar is the ISO 15693, often used to represent the 13.56 MHz UHF technology technical characteristics and were compared with the foundation . ISO 15693 in the past was used for non- contact smart card standard. Now a lot of interoperable products ISO 15693 tags and readers , has also been used for other purposes, including commercial laundry tracking , library management , file tracking and sample identification .
Another major 13.56 MHz standard ISO 14443. Past, mainly for non-contact charging and other electronic payments, is now used for large-scale public transport system . And for a single product Level Management ISO 18000 series of standards , including a feature called the 13.56 MHz ISO 18000-3 standard . This standard prior to ISO 18000-6 UHF Series ( Note : includes EPC Gen 2, equivalent to ISO 18000-6 Part C).
Because 13.56 MHz are the first one to be standardized RFID technology while getting strong support from vendors , they were a lot of use . Some foresee contactless identification and high-speed read and write will bring great benefits to businesses , you try to 13.56 MHz technology for the distribution and other supply chain management. However , due to the limited read range , 13.56 MHz technology does not support efficient packaging and pallet management operations , nor conducive to the implementation UHF EPC Gen 2 and other supply chain standards . These early applications have also hindered the development and adoption of RFID technology . 13.56 MHz technology existence of these shortcomings, some people will come to this conclusion : Taken together , RFID technology is not a reliable and effective technique . This misconception although countless success stories UHF negated , but there still exists.
UHF RFID technology
Most UHF RFID systems are running at 858-930 MHz frequency band and transmit data through the RF propagation , the maximum read range between 20 and 30 feet . One of the rare, commercialization is close UHF systems , transmission of data in the electromagnetic field , and is suitable for short-range reading . UHF standard is very large, but most are Gen 2 - the most support for RFID standards .
UHF in the supply chain management is the dominant technology - such as in the case and pallet tracking, returnable container identification , it is also widely used in industrial automation , business process tracking, asset management, inventory control , transportation monitoring , identification, depot management and document security and other fields.
Early applications in the UHF system , there are a lot of people think: This technique can not be used in liquid or metallic material . But today , this technology has been to break through this bottleneck. Some UHF tags have been used for metal materials, and the use of metal conductivity improves RF performance. In addition, the antenna design , the reader FM advances are gradually overcoming the traditional limitations.
The need for new thinking to treat HF and UHF
The maturity is technically conventional HF and UHF debate one of the reasons is no longer applicable . Conventional wisdom holds that : UHF most suitable long distance reading , while the HF is the most appropriate level of short-range identification of a single product , or for liquids or metal materials. This view is an oversimplification of how to choose the most appropriate business processes and technology processes, which may restrict certain technology was selected opportunities.
For example, the read range and can not decide in the end you should use UHF or HF technology . UHF system does not need to be a close reading technology - read range of 30 feet can be used to label the range of 1 inch . UHF systems can adjust the location and configuration of the reader , to read from a variety of processes and optimized under utilized. Because UHF can provide the user needs to read from the range, so often used as a business process tracking, case and pallet identification , access control , inventory control and security management. In addition , there is no proof of Physics and Technology, this technique can not be used because short reads.
End users to really understand their needs is the key to resolving this dispute
If the long distance read , 13.56 MHz technology is not applicable because it is not applicable for read range UHF technology . Therefore, the deployment of this system should be considered an extension of RFID technology . For example, if the RFID tag was originally used to identify low-capacity of a single product , and is a hand held reader to read , then the 13.56 MHz technology will be very applicable . But if it is used for unattended , high-speed business processes - such as reading a single product on the conveyor label, long- distance technology becomes an advantage. Which one can not consider selecting frequency , businesses should choose a single frequency to avoid duplication labeling .
For a long time , 13.56 MHz technology has been used as a single product -level labeling, but recently it was discovered , UHF technology can also be used to identify a single product . We can consider the following example:
Pan-European retailer METRO Group will Gen 2 UHF tag is used in high-speed systems clothing single product library can be completed per hour 8000 clothing label . British retailer Marks and Spencer has been the number one UHF item-level labeling for 35 million products. Boeing says it will use a permanent 787 UHF tags for fantasy about 1700-2000 pieces parts inside label . Cardinal Health Company also announced the adoption of a single product level UHF tags to meet the electronic pedigree requirements. American Sushi Restaurant Blue C Sushi also using UHF tags to track food dish single product , read the distance is less than one foot . UHF is also used documents, identification cards , which were previously used 13.56 MHz technologies. The U.S. State Department also used as a passport project Gen 2 standards. UHF NEXUS system is also used to identify norms U.S. immigration officers .
Many of these companies have adopted Gen 2 UHF system for crates and pallets level business . By using UHF item-level technology, these manufacturers can take advantage of their system , without the need for additional facilities .
Still the concept is outdated
The idea that HF technology is used in metal and liquid materials view is not very realistic. In supply chain management , UHF often used to identify the liquid content or metal crates and pallets identification .
Hong Kong International Airport provides us with a good example - this is one of the few in the world using Gen 2 RFID to identify, manage one airport baggage . The management system includes metallic materials - requires close contact with the reader labeling bags .
Newest and largest airport in Southeast Asia - Thailand, Bangkok airport is also used UHF RFID tag identification mark out of a suitcase . Trunk itself has a lot of metal, but UHF RFID tag can still be read.
UHF reliability in these materials can be extended to a single product level - in the pharmaceutical industry , UHF label foil packaging for liquid medications identification . Item-level UHF tags are recognized for packaging , product certification , etc. , many of which are required to use thousands of SKUs read simultaneously.
Another example of the same description of the problem, in the tests of HF and UHF technology, select UHF tag identification Boeing aircraft parts , the status of the investigation before takeoff . These aircraft parts are usually to be read at close range , during which there will be metal or other interference factors. Boeing metal UHF tag identification metal objects - which in the past , few people would think .
These examples above have proven RFID technology and its applications is how evolution , but also showed why the previous limitations of the technology point of view is no longer applicable . If only to look all the limitations placed on technology , they will deny the importance of the development process , which is not conducive to the realization of business value . RFID technology will continue to evolve according to demand progress.
The core value lies in RFID Process Services
If the direct barcode technology RFID technology as a replacement or strictly satisfy the matching command , then the cost of RFID technology not seen for a bargain. As we mentioned earlier, the use of the 13.56 MHz technology , RFID was initially thought to not be used for supply chain management. Businesses can scan bar code system in their distance range , 13.56 MHz tags successfully read . Therefore, the new process does not develop .
Today, many processes including the use of bar code reader to read conveyors , handling machines and manual handling stickers barcode objects , and it will adjust the barcode position in order to facilitate reading . RFID technology because it can be non- linear read labels , and can recognize multiple objects simultaneously , thus reducing the labor input . RFID technology reads the wider the range of the object position requirements are lower - and thus will be more likely to create labor-saving business processes. This is also the RFID technology is superior to barcode technology places . For example , the barcode ID will often limit the performance of transmission systems , as transfer machines generally will operate at speeds less than the maximum so that the bar code reader to read the object in transmission .
If the user is not careful planning can bring business value of business processes in the case , on the choice of a technique that results may be disappointing. And consider the future needs of an RFID technique to be used for different purposes , is very important. For example , early WIP tracking for RFID projects can be extended to inventory and shipment tracking . Moreover, refinement UHF technology and to meet short CSCL to read , and the storage , transportation and long distance receiving process reads .
Thus, based on HF and UHF technology , arguing whether the technology is mature and has been standardized , or debate them in the right circumstances can play with the excellent performance and reliable , they are not much significance. We want to argue that, for each technology , the best use of what is the effect ; effectively understand and meet business needs as well as the depth of excavation RFID ROI is most important. If the end user can truly understand their needs , they should be adopted without debate in the end what technology it.